Hi every one...Today i am here again with another very important article for beginners.in this article we are going to discuss about some commonly used electronic component and their symbols. you must be familiarized with these symbols for better understanding of circuit diagrams.
WIRES
Simple wire
Used to connect one component to another.
Wire joined
One device may be connected to another through wires. This is represented by drawing “blobs” on the point where they are shorted.

Wire not joined
When circuits are drawn some wires may not touch others. This can only be shown by bridging them or by drawing them without blobs. But bridging is commonly practised as there will not arise any confusion.
When circuits are drawn some wires may not touch others. This can only be shown by bridging them or by drawing them without blobs. But bridging is commonly practised as there will not arise any confusion.

RESISTORS
Resistor
A resistor is used to restrict the amount of current flow through a device. Abbreviated as ‘R’.
 |
| resistor |
A rheostat is used to control the current flow with two contacts. Applicable in controlling lamp brightness, capacitor charge rate, etc.

Potentiometer
A potentiometer is used to control the voltage flow and has three contacts. Have applications in changing a mechanical angle change to an electrical parameter. Abbreviated as ‘POT’.

Preset
Presets are low cost variable resistors that are used to control the charge flow with the help of a screw driver. Applications where the resistance is determined only at the end of the circuit design.

CAPACITORS
Capacitor
Capacitor is a device that is used to store electrical energy. It consists of two metals plates that are separated by a dielectric. It is applicable as a filter, that is, to block DC signals and allow AC signals. Abbreviated with the letter ‘C’.

Polarized capacitor
Polarized Capacitor can be used in a timer circuit by adding a resistor.

Variable capacitor
Used to vary the capacitance by turning the knob. A type of variable capacitor is the trimmer capacitor that is small in size. The notations are all the same.

POWER SUPPLY
Cell
Used to provide a supply for a circuit.
Cell
Used to provide a supply for a circuit.

Battery
A battery has more than a cell and is used for the same purpose. The smaller terminal is negative and the larger one is positive. Abbreviated as ‘B’.

DC supply
Used as a DC power supply, that is, the current will always flow in one direction.

AC Supply
Used as AC power supply, that is, the current will keep alternating directions.

Fuse
Used in circuits where a probability of excessive current flows. The fuse will break the circuit if excessive current flows and saves the other devices from damage.
Used in circuits where a probability of excessive current flows. The fuse will break the circuit if excessive current flows and saves the other devices from damage.

Transformer
Used as an ac power supply. Consists of two coils, the primary and secondary that are linked together through an iron core. There is no physical connection between the two coils. The principle of mutual inductance is used to obtain power. Abbreviated as ‘T’.

Ground
Used in electronic circuits to represent the 0 volts of the power supply. It can also be defined as the real earth , when it is applied in radio circuits and power circuits.

DIODES
Diode
A diode is used to allow electric current to flow in only one direction. Abbreviated as ‘D’.
Diode
A diode is used to allow electric current to flow in only one direction. Abbreviated as ‘D’.

LED
is used to emit light when a current is passed through the device. It is abbreviated as LED.

Photo diode
works as a photo-detector and converts light into its corresponding voltage or current.

Zener Diode
After a breakdown voltage, the device allows current to flow in the reverse direction as well. It is abbreviated as ‘Z’.

TRANSISTORS
NPN
This is a transistor with a layer of P-doped semiconductor fixed between two layers of N-doped semiconductors that act as the emitter and collector. Abbreviated as ‘Q’.
NPN
This is a transistor with a layer of P-doped semiconductor fixed between two layers of N-doped semiconductors that act as the emitter and collector. Abbreviated as ‘Q’.

PNP
This is a transistor with a layer of N-doped semiconductor fixed between two layers of P-doped semiconductors that act as the emitter and collector. Abbreviated as ‘Q’.

Photo transistor
The working of a it is similar to that of a bipolar transistor with a difference that it converts light into its corresponding current. The photo transistor can also act as a photo diode if the emitter is not connected.

OUT PUT DEVICES
Lighting lamp
This is used to provide light for the output.
Lighting lamp
This is used to provide light for the output.

Indicator lamp
Used to convert electrical energy into light. The best example is the warning light on a car dashboard.

Heater
This transducer is used to change electrical energy into heat.

Inductor
Inductor is used to produce a magnetic field when a certain current is passed through a coil of wire. The wire is coiled on a soft iron core. Have applications in motors, and tank circuits. Abbreviated as ‘L’.

This device is used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Can be used as a generator as well. Abbreviated as ‘M’.

Bell
Used to produce a sound as the output, according to the electrical energy produced as the input.

Buzzer
It is used to produce an output sound corresponding to the electrical energy in the input.

SENSORS
LDR
It is abbreviated as LDR.light dependent resistor is used to convert light into its corresponding resistance. Instead of directly measuring the light, it senses the heat content and converts it onto resistance.

Thermistor
Instead of directly measuring the light, a thermistor senses the heat content and converts it into resistance. Abbreviated as ‘TH’.

METERS
Voltmeter
is used to measure the voltage at a certain point in the circuit.
Voltmeter
is used to measure the voltage at a certain point in the circuit.

Ammeter
An Ammeter is used to measure the current that passes through the circuit at a particular point.

Galvanometer
is used to measure very small currents in the order of 1 milli ampere or less.

Ohmmeter
Resistance of the circuit is measured using an Ohmmeter.

Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope is used to measure the voltage and time period of signals along with their shape display.
An oscilloscope is used to measure the voltage and time period of signals along with their shape display.

LOGIC GATES
AND
If all the inputs of an AND gate are HIGH, then the output will also be HIGH. If any one of them is LOW, the output will also be LOW.

OR
If any one of the input is HIGH, the output will also be HIGH. If both inputs are LOW, the output will also be LOW.

NOT
Also known as the inverter Gate. There is only one input for this gate. If the input is HIGH, the output will be LOW. If the input is LOW, the output will be HIGH.

NAND
Short form for NOT AND Gate. Of all the inputs are HIGH, the output will be LOW. If any one input is LOW, the output will be HIGH.

NOR
Short form for NOT OR. If both inputs are LOW, the output will also be LOW. For other cases, the output will be HIGH.

EX-0R
Short form for Exclusive NOR. If both inputs are either in LOW state r HIGH state, the output will be LOW. If both inputs are different, the output will be HIGH.

EX-NOR
Short form for Exclusive NOT OR. If both the inputs are the same, the output will be HIGH. If both are different, the output will also be different.

SWITCHES
Push Switch
This is an ordinary switch that passes current only upon pressing.

Push to Break Switch
The push to break switch is usually kept in the ON state (closed). It turns to OFF state (open) only when the switch is pressed.
 |
Singe Pole Single Throw Switch
Also known as the ON/OFF switch. This switch allows the flow of current only when it is kept ON. Abbreviated as SPST.

Single Pole Double Throw Switch
Also known as the 2-way switch. It can be also called as an ON/OFF/ON switch as it has an OFF position in the center. The switch causes the flow of current in two directions, depending on its position. It can be abbreviated as SPDT.

Double Pole Single Throw Switch
Abbreviated as DPST. Can also be called as a dual ON-OFF switch. This is used to isolate between the live and neutral connections in the main electrical line.
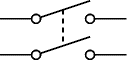
Double Pole Double Throw Switch
Abbreviated as DPDT. The switch uses a central OFF position and is applied as reversing switch for motors.

Relay
is abbreviated as ‘RY’. This device can easily switch a 230 Volt AC mains circuit. It has three switching stages called Normally Open (NO). Normally Closed (NC), and Common (COM).

AUDIO AND RADIO DEVICES
Microphone
This device is used for converting sound to its corresponding electrical energy. Abbreviated as ‘MIC’.

Earphone
Does the reverse process of microphone and converts electrical energy into sound.
Does the reverse process of microphone and converts electrical energy into sound.

Loudspeaker
Does the same operation as an earphone, but converts an amplified version of the electrical energy into its corresponding sound.

Piezo-Transducer
It is a transducer that converts electrical energy into sound.

Amplifier
Used to amplify a signal. It is mainly used to represent a whole circuit rather than just one component.

Aerial
This device is used to transmit/receive signals. Abbreviated as ‘AE’.













0 comments:
Post a Comment